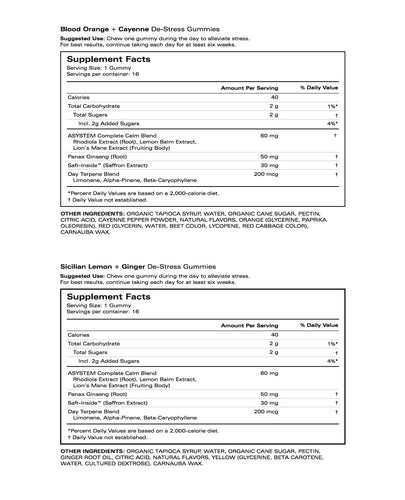
asystem-wellness.myshopify.com
[{"id":6619438383297,"title":"Calm Gummies","handle":"complete-calm-destress","description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eCalm you can feel — without the pills.\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eThese gummies help you manage stress and unwind, naturally.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eFormulated with clinically studied ingredients like Sensoril® Ashwagandha, Chamomile, Affron®, and soothing botanicals like Lemon Balm and Holy Basil to help you relax and reset.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eTake two gummies daily to ease tension and support a balanced, relaxed mind.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2021-03-30T16:37:32-04:00","created_at":"2021-03-30T16:21:45-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Consumable","tags":["Gummy"],"price":5900,"price_min":5900,"price_max":5900,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":39557338038465,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-CALM-60CT","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Calm Gummies","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":5900,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"850014293376","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":4720}],"price":4720,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":4720,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1763351679","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1763351679","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1763351679","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1763351679"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1763351679","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":42320425484528,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1763351679"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1763351679","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42320425451760,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1763351679"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1763351679","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42320425418992,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1763351679"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1763351679","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42320425386224,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1763351679"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/CALM_Gummies_2025_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1763351679","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[{"id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836","name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"values":["30 Days"]}],"selling_plans":[{"id":7042990320,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save 20%","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"30 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":20}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}}],"app_id":"5859381"}],"content":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eCalm you can feel — without the pills.\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eThese gummies help you manage stress and unwind, naturally.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eFormulated with clinically studied ingredients like Sensoril® Ashwagandha, Chamomile, Affron®, and soothing botanicals like Lemon Balm and Holy Basil to help you relax and reset.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eTake two gummies daily to ease tension and support a balanced, relaxed mind.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":8231984595184,"title":"Focus Gummies","handle":"productivity-gummies-2","description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eYour brain’s new secret weapon for getting stuff done.\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e ✅ 5+ hours of clean, focused energy*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e ⚡ Zero crash, zero jitters*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e 💡 Stay sharp, alert, and in the zone*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003ePowered by a patented form of L-theanine (Suntheanine®), slow-releasing caffeine (NewCaff®), mango leaf extract (Zynamite®), NAD, and more to fuel smooth, steady focus — no jitters, no burnout, just effortless productivity.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2023-03-09T16:36:28-05:00","created_at":"2023-03-06T12:14:17-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Consumable","tags":[],"price":5900,"price_min":5900,"price_max":5900,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":43888157950192,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-FOCUS-60CT","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Focus Gummies","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":5900,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"850014293406","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":4720}],"price":4720,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":4720,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1_684a9c00-d1d4-4d71-828e-13ae615a0c08.jpg?v=1766160546","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1766160546","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1766160546","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1766160546"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1_684a9c00-d1d4-4d71-828e-13ae615a0c08.jpg?v=1766160546","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":42923719590128,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1_684a9c00-d1d4-4d71-828e-13ae615a0c08.jpg?v=1766160546"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1_684a9c00-d1d4-4d71-828e-13ae615a0c08.jpg?v=1766160546","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42463952929008,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1766160546"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1766160546","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42463952896240,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1766160546"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1766160546","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42463952863472,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1766160546"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/FOCUS_Gummies_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1766160546","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[{"id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836","name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"values":["30 Days"]}],"selling_plans":[{"id":7042990320,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save 20%","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"30 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":20}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}}],"app_id":"5859381"}],"content":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eYour brain’s new secret weapon for getting stuff done.\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e ✅ 5+ hours of clean, focused energy*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e ⚡ Zero crash, zero jitters*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan\u003e 💡 Stay sharp, alert, and in the zone*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003ePowered by a patented form of L-theanine (Suntheanine®), slow-releasing caffeine (NewCaff®), mango leaf extract (Zynamite®), NAD, and more to fuel smooth, steady focus — no jitters, no burnout, just effortless productivity.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":9689556353264,"title":"Women's Complete Optimization","handle":"womens-complete-optimization","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eFeel Your Best Every Day\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cbr\u003e30 days of sustained energy, stress relief, immune support, and cellular vitality—all in one convenient daily packet.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cul\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eBoost Energy \u0026amp; Vitality:\u003c\/strong\u003e Supports steady, lasting energy so you can power through your day without crashes.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eSupport Stress Resilience:\u003c\/strong\u003e Helps promote calm, even during high-stress days.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eStrengthen Immunity:\u003c\/strong\u003e Clinically backed ingredients help your body defend against daily challenges.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003ePromote Healthy Aging:\u003c\/strong\u003e Supports cellular repair, mitochondrial function, and overall longevity.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eEase Inflammation \u0026amp; Support Mood:\u003c\/strong\u003e Helps your body recover, think clearly, and feel balanced.*\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003c\/ul\u003e","published_at":"2025-11-03T10:32:28-05:00","created_at":"2025-10-15T14:41:05-04:00","vendor":"asystem-wellness","type":"One Time Purchase","tags":["mh_sync","no-shipping-label-for-uk-can","NonCore","One Time"],"price":9900,"price_min":9900,"price_max":9900,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":48175819325680,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-COSW-30D-M1","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Women's Complete Optimization","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":9900,"weight":487,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":7920}],"price":7920,"compare_at_price":9900,"per_delivery_price":7920,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_1_9c1742cd-a46d-42f3-bbc2-e6eb4b2a6eb0.jpg?v=1763400271","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_3_3d6ff7e5-3986-49fb-aa4a-9e8f8dd86e46.jpg?v=1763400271","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_4_28fda910-ba03-482d-8e48-4bbda3c3f845.jpg?v=1763400271","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_2_38175554-83c4-4103-ac16-4487a60316a0.jpg?v=1763400271"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_1_9c1742cd-a46d-42f3-bbc2-e6eb4b2a6eb0.jpg?v=1763400271","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":42327004250352,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_1_9c1742cd-a46d-42f3-bbc2-e6eb4b2a6eb0.jpg?v=1763400271"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_1_9c1742cd-a46d-42f3-bbc2-e6eb4b2a6eb0.jpg?v=1763400271","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42110311432432,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_3_3d6ff7e5-3986-49fb-aa4a-9e8f8dd86e46.jpg?v=1763400271"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_3_3d6ff7e5-3986-49fb-aa4a-9e8f8dd86e46.jpg?v=1763400271","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42110311399664,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_4_28fda910-ba03-482d-8e48-4bbda3c3f845.jpg?v=1763400271"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_4_28fda910-ba03-482d-8e48-4bbda3c3f845.jpg?v=1763400271","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42327004283120,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_2_38175554-83c4-4103-ac16-4487a60316a0.jpg?v=1763400271"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Womens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_COPW_PDP_Lifestyle_2_38175554-83c4-4103-ac16-4487a60316a0.jpg?v=1763400271","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[{"id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836","name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"values":["30 Days"]}],"selling_plans":[{"id":7042990320,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save 20%","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"30 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":20}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}}],"app_id":"5859381"}],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eFeel Your Best Every Day\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cbr\u003e30 days of sustained energy, stress relief, immune support, and cellular vitality—all in one convenient daily packet.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cul\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eBoost Energy \u0026amp; Vitality:\u003c\/strong\u003e Supports steady, lasting energy so you can power through your day without crashes.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eSupport Stress Resilience:\u003c\/strong\u003e Helps promote calm, even during high-stress days.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eStrengthen Immunity:\u003c\/strong\u003e Clinically backed ingredients help your body defend against daily challenges.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003ePromote Healthy Aging:\u003c\/strong\u003e Supports cellular repair, mitochondrial function, and overall longevity.*\u003cbr\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\n\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003cli\u003e\n\u003cstrong\u003eEase Inflammation \u0026amp; Support Mood:\u003c\/strong\u003e Helps your body recover, think clearly, and feel balanced.*\u003c\/li\u003e\n\u003c\/ul\u003e"},{"id":1920854982719,"title":"Complete Optimization for Men","handle":"mens-essentials-system","description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eMeet Your Daily Edge – 30 Days of Complete Optimization in 5 Powerful Capsules\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eUnlock peak performance with Complete Optimization Supplements — a powerhouse blend of 30+ clinically studied vitamins, minerals, adaptogens, and omegas to fuel your energy, immunity, focus, strength, and libido.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eOne box contains 30 pre-measured daily packs. No guesswork. No clutter. All convenience — just five targeted capsules a day to keep you optimized, resilient, and ready.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2023-06-27T14:04:32-04:00","created_at":"2019-07-15T18:51:57-04:00","vendor":"asystem-wellness","type":"One Time Purchase","tags":["label:for men","mh_sync","no-shipping-label-for-uk-can","NonCore","One Time"],"price":9900,"price_min":9900,"price_max":9900,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":48175966748912,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-COS-30D-1N","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Complete Optimization for Men","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":9900,"weight":487,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"850014293000","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":7920}],"price":7920,"compare_at_price":9900,"per_delivery_price":7920,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1766072648","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1766072648","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1766072648","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1766072789","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_6.jpg?v=1766072789","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_7.jpg?v=1766072789","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1766072789","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_8.jpg?v=1766072789","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_9.jpg?v=1766072789"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1766072648","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":42910660428016,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1766072648"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1766072648","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660559088,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1766072648"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1766072648","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660493552,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1766072648"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1766072648","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660460784,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1766072789"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1766072789","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660591856,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_6.jpg?v=1766072789"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_6.jpg?v=1766072789","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660624624,"position":6,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_7.jpg?v=1766072789"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_7.jpg?v=1766072789","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660526320,"position":7,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1766072789"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1766072789","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660657392,"position":8,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_8.jpg?v=1766072789"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_8.jpg?v=1766072789","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":42910660690160,"position":9,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_9.jpg?v=1766072789"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Mens_Complete_Opt_Supp_2025_PDP_Lifestyle_9.jpg?v=1766072789","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[{"id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836","name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"values":["30 Days"]}],"selling_plans":[{"id":7042990320,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save 20%","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"30 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":20}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}}],"app_id":"5859381"}],"content":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eMeet Your Daily Edge – 30 Days of Complete Optimization in 5 Powerful Capsules\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eUnlock peak performance with Complete Optimization Supplements — a powerhouse blend of 30+ clinically studied vitamins, minerals, adaptogens, and omegas to fuel your energy, immunity, focus, strength, and libido.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eOne box contains 30 pre-measured daily packs. No guesswork. No clutter. All convenience — just five targeted capsules a day to keep you optimized, resilient, and ready.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":8370566627568,"title":"Sleep Gummies + Melatonin","handle":"complete-calm-melatonin-sleep-gummies","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eAn advanced all natural sleep gummy. Perfect for jet lag or anyone needing some better zzz's. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eClinically studied to help fall asleep fast, improve sleep quality, and wake up free of grogginess.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eMade with botanicals, adaptogens, and clinically studied ingredients like \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eSafr-Inside™, PhytoMelatonin, Chamomile, Passionflower, Holy Basil, and more. *\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2023-10-31T15:05:31-04:00","created_at":"2023-10-31T15:02:57-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Consumable","tags":["Gummy"],"price":3500,"price_min":3500,"price_max":5900,"available":true,"price_varies":true,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":44354525790448,"title":"32 Gummies","option1":"32 Gummies","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"CCS-WBM-32D-M1","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Sleep Gummies + Melatonin - 32 Gummies","public_title":"32 Gummies","options":["32 Gummies"],"price":5900,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":4720}],"price":4720,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":4720,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]},{"id":44354525888752,"title":"Two Refills (32 Gummies)","option1":"Two Refills (32 Gummies)","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"CCS-WBM-32D-MR","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Sleep Gummies + Melatonin - Two Refills (32 Gummies)","public_title":"Two Refills (32 Gummies)","options":["Two Refills (32 Gummies)"],"price":5900,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":4720}],"price":4720,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":4720,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]},{"id":44354525855984,"title":"Travel Tin (16 Gummies)","option1":"Travel Tin (16 Gummies)","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-CCS-WBWM-16D-2","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Sleep Gummies + Melatonin - Travel Tin (16 Gummies)","public_title":"Travel Tin (16 Gummies)","options":["Travel Tin (16 Gummies)"],"price":3500,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"850014293109","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":2800}],"price":2800,"compare_at_price":3500,"per_delivery_price":2800,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-08.jpg?v=1743521534","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-09.jpg?v=1743521534","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-10.jpg?v=1743521534","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-11.jpg?v=1743521534"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-08.jpg?v=1743521534","options":["Pick Your Pack"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":39145388278000,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-08.jpg?v=1743521534"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-08.jpg?v=1743521534","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39145388343536,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-09.jpg?v=1743521534"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-09.jpg?v=1743521534","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39145388376304,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-10.jpg?v=1743521534"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-10.jpg?v=1743521534","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39145388409072,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-11.jpg?v=1743521534"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-11.jpg?v=1743521534","width":1250}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[{"id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836","name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"values":["30 Days"]}],"selling_plans":[{"id":7042990320,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save 20%","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"30 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":20}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}}],"app_id":"5859381"}],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eAn advanced all natural sleep gummy. Perfect for jet lag or anyone needing some better zzz's. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eClinically studied to help fall asleep fast, improve sleep quality, and wake up free of grogginess.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eMade with botanicals, adaptogens, and clinically studied ingredients like \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eSafr-Inside™, PhytoMelatonin, Chamomile, Passionflower, Holy Basil, and more. *\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":4485572952127,"title":"Radical Relief Gel Roll On","handle":"gel-roll-on","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eThe most powerful, instant pain-fighting topical on the market. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eTested and used by athletes for workout recovery, viral for PMS cramp relief. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003ePacked with \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003ea unique blend of muscle-soothing clinical, natural, and\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e 25% active ingredients (that’s 5x more than anyone else) like Menthol, Methyl Salicylate, Arnica Montana Oil, Pinus Pinaster Bark, and Vitamin E. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eOur Radical Relief Gel Roll On works instantly to relieve pain. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eWhether you’ve got muscle aches, period cramps, or even headaches this soothing wonder releases a cooling sensation followed by warmth and features a cryosphere applicator \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eto massage directly into your muscles and joints, further releasing tension.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003ca rel=\"noopener\" title=\"Radical Relief Gel Roll On Drug Facts\" href=\"https:\/\/cdn.shopify.com\/s\/files\/1\/0085\/4061\/8815\/files\/GROsupplementfacts-2024.jpg?v=1720727228\" target=\"_blank\"\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eIngredient List\u003c\/span\u003e (click here)\u003c\/a\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cdiv\u003e\u003c\/div\u003e\n\u003cstyle type=\"text\/css\"\u003e\u003c!--\ntd {border: 1px solid #ccc;}br {mso-data-placement:same-cell;}\n--\u003e\u003c\/style\u003e","published_at":"2023-09-21T12:19:02-04:00","created_at":"2020-02-10T22:16:22-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"One Time Purchase","tags":["no-shipping-label-for-uk-can"],"price":4900,"price_min":4900,"price_max":4900,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":31780335517759,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-GR-30D-2","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Radical Relief Gel Roll On","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":4900,"weight":363,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"850014293024","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":3920}],"price":3920,"compare_at_price":4900,"per_delivery_price":3920,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743517995","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-05.jpg?v=1743517995","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-06.jpg?v=1743517995","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-07.jpg?v=1743517995"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743517995","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":39144696873200,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743517995"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743517995","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39144696938736,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-05.jpg?v=1743517995"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-05.jpg?v=1743517995","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39144696905968,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-06.jpg?v=1743517995"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-06.jpg?v=1743517995","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39144697004272,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-07.jpg?v=1743517995"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/GRO_PDP_edits-07.jpg?v=1743517995","width":1250}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[{"id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836","name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"values":["30 Days"]}],"selling_plans":[{"id":7042990320,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save 20%","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"30 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":20}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}}],"app_id":"5859381"}],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eThe most powerful, instant pain-fighting topical on the market. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eTested and used by athletes for workout recovery, viral for PMS cramp relief. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003ePacked with \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003ea unique blend of muscle-soothing clinical, natural, and\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e 25% active ingredients (that’s 5x more than anyone else) like Menthol, Methyl Salicylate, Arnica Montana Oil, Pinus Pinaster Bark, and Vitamin E. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eOur Radical Relief Gel Roll On works instantly to relieve pain. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eWhether you’ve got muscle aches, period cramps, or even headaches this soothing wonder releases a cooling sensation followed by warmth and features a cryosphere applicator \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eto massage directly into your muscles and joints, further releasing tension.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003ca rel=\"noopener\" title=\"Radical Relief Gel Roll On Drug Facts\" href=\"https:\/\/cdn.shopify.com\/s\/files\/1\/0085\/4061\/8815\/files\/GROsupplementfacts-2024.jpg?v=1720727228\" target=\"_blank\"\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eIngredient List\u003c\/span\u003e (click here)\u003c\/a\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cdiv\u003e\u003c\/div\u003e\n\u003cstyle type=\"text\/css\"\u003e\u003c!--\ntd {border: 1px solid #ccc;}br {mso-data-placement:same-cell;}\n--\u003e\u003c\/style\u003e"},{"id":9808355852528,"title":"Relax \u0026 Refocus Bundle","handle":"relax-refocus-bundle","description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eDiscover the perfect balance for your mind and body. This thoughtfully curated bundle combines our \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eCALM Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e, designed to soothe stress and support relaxation, with our \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eFOCUS Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e, crafted to enhance mental clarity and sustained concentration. Together, they create a harmonious daily ritual. Stay centered, alert, and ready to thrive, no matter the demands of your day.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2026-01-09T12:36:49-05:00","created_at":"2026-01-07T19:20:05-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":9440,"price_min":9440,"price_max":9440,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":11800,"compare_at_price_min":11800,"compare_at_price_max":11800,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":48686547075312,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":null,"requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Relax \u0026 Refocus Bundle","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":9440,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":11800,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_fc55521e-7cbb-4fa5-89dd-c39525e9fb67.jpg?v=1768415833","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415833","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415833","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415833"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_fc55521e-7cbb-4fa5-89dd-c39525e9fb67.jpg?v=1768415833","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":43215871705328,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_fc55521e-7cbb-4fa5-89dd-c39525e9fb67.jpg?v=1768415833"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_fc55521e-7cbb-4fa5-89dd-c39525e9fb67.jpg?v=1768415833","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151779430640,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415833"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415833","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151779463408,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415833"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415833","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151779496176,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415833"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Relax_Refocus_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415833","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eDiscover the perfect balance for your mind and body. This thoughtfully curated bundle combines our \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eCALM Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e, designed to soothe stress and support relaxation, with our \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eFOCUS Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e, crafted to enhance mental clarity and sustained concentration. Together, they create a harmonious daily ritual. Stay centered, alert, and ready to thrive, no matter the demands of your day.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":9808359162096,"title":"The Glow \u0026 Go Bundle","handle":"the-glow-go-bundle","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cmeta charset=\"UTF-8\"\u003eElevate your wellness with the ultimate curated trio for women. This sophisticated bundle combines \u003cstrong\u003eWomen’s Complete Optimization Supplements, Radial Relief Gel Roll-On, and FOCUS Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e to support total vitality, targeted relief, and enhanced mental clarity. Designed for the modern woman who seeks precision, balance, and effortless optimization, each product works synergistically to refine your body, sharpen your mind, and restore your energy. Luxury wellness, thoughtfully delivered.*\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2026-01-09T12:36:50-05:00","created_at":"2026-01-07T19:24:44-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":16560,"price_min":16560,"price_max":16560,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":20700,"compare_at_price_min":20700,"compare_at_price_max":20700,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":48686552580336,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":null,"requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"The Glow \u0026 Go Bundle","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":16560,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":20700,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_bad23a60-da48-4bd2-ac51-0731ebbefc76.jpg?v=1768415779","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415779","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415779","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415779","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1768415779"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_bad23a60-da48-4bd2-ac51-0731ebbefc76.jpg?v=1768415779","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":43215859056880,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_bad23a60-da48-4bd2-ac51-0731ebbefc76.jpg?v=1768415779"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1_bad23a60-da48-4bd2-ac51-0731ebbefc76.jpg?v=1768415779","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151923380464,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415779"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415779","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151923347696,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415779"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415779","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151923446000,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415779"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415779","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151923413232,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1768415779"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Glow_Go_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1768415779","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cmeta charset=\"UTF-8\"\u003eElevate your wellness with the ultimate curated trio for women. This sophisticated bundle combines \u003cstrong\u003eWomen’s Complete Optimization Supplements, Radial Relief Gel Roll-On, and FOCUS Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e to support total vitality, targeted relief, and enhanced mental clarity. Designed for the modern woman who seeks precision, balance, and effortless optimization, each product works synergistically to refine your body, sharpen your mind, and restore your energy. Luxury wellness, thoughtfully delivered.*\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":9808359948528,"title":"The Power Pair Bundle","handle":"the-power-pair-bundle","description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eExperience daily wellness refined for both him and her. This premium duo brings together targeted, all-in-one formulations designed to support energy, focus, resilience, immune health, and foundational vitality, with ingredients and blends tailored specifically to male and female physiology. Our \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWomen's Complete Optimization\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e delivers over 80+ essential vitamins, minerals, and clinically backed adaptogens to help women thrive with sustained energy, stress support, and cellular vitality. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eMen's Complete Optimization\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e offers a potent blend of adaptogens, omegas, and performance-focused compounds to enhance men’s strength, focus, recovery, and overall well-being. Together, they form a complete daily optimization ritual crafted for balance, longevity, and elevated living.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2026-01-09T12:36:51-05:00","created_at":"2026-01-07T19:30:51-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":15840,"price_min":15840,"price_max":15840,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":19800,"compare_at_price_min":19800,"compare_at_price_max":19800,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":48686555267312,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":null,"requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"The Power Pair Bundle","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":15840,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":19800,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1767897633","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1767897633","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1767897633","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1767897633"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1767897633","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":43151938388208,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1767897633"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1767897633","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151938420976,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1767897633"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1767897633","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151938453744,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1767897633"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1767897633","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151938486512,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1767897633"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Power_Pair_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1767897633","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eExperience daily wellness refined for both him and her. This premium duo brings together targeted, all-in-one formulations designed to support energy, focus, resilience, immune health, and foundational vitality, with ingredients and blends tailored specifically to male and female physiology. Our \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWomen's Complete Optimization\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e delivers over 80+ essential vitamins, minerals, and clinically backed adaptogens to help women thrive with sustained energy, stress support, and cellular vitality. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eMen's Complete Optimization\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003cspan\u003e offers a potent blend of adaptogens, omegas, and performance-focused compounds to enhance men’s strength, focus, recovery, and overall well-being. Together, they form a complete daily optimization ritual crafted for balance, longevity, and elevated living.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":9808359260400,"title":"The Sharp \u0026 Steady Bundle","handle":"the-sharp-steady-bundle","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cmeta charset=\"UTF-8\"\u003eA complete daily system for peak performance, inside and out. This bundle pairs \u003cstrong\u003eMen’s Complete Optimization Supplements\u003c\/strong\u003e for foundational vitality, \u003cstrong\u003eFOCUS Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e for clean mental clarity, and the \u003cstrong\u003eRadial Relief Gel Roll\u003c\/strong\u003e On for fast-acting muscle and joint support. Designed to help you think sharper, move better, and recover smarter.*\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2026-01-09T12:36:50-05:00","created_at":"2026-01-07T19:27:38-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":16560,"price_min":16560,"price_max":16560,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":20700,"compare_at_price_min":20700,"compare_at_price_max":20700,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":48686552842480,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":null,"requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"The Sharp \u0026 Steady Bundle","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":16560,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":20700,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1768415727","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415727","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415727","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415727","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1768415727"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1768415727","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":43215853945072,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1768415727"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/New_Product_Bundle_PDP_PDP_Lifestyle_1.jpg?v=1768415727","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151877177584,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415727"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_2.jpg?v=1768415727","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151877210352,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415727"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_3.jpg?v=1768415727","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151877243120,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415727"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_4.jpg?v=1768415727","width":2500},{"alt":null,"id":43151877275888,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"width":2500,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1768415727"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":2500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Sharp_Steady_Bundle_PDP_Lifestyle_5.jpg?v=1768415727","width":2500}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cmeta charset=\"UTF-8\"\u003eA complete daily system for peak performance, inside and out. This bundle pairs \u003cstrong\u003eMen’s Complete Optimization Supplements\u003c\/strong\u003e for foundational vitality, \u003cstrong\u003eFOCUS Gummies\u003c\/strong\u003e for clean mental clarity, and the \u003cstrong\u003eRadial Relief Gel Roll\u003c\/strong\u003e On for fast-acting muscle and joint support. Designed to help you think sharper, move better, and recover smarter.*\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":9141443461360,"title":"Workout Optimization Bundle","handle":"the-athletes-tool-kit","description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eLevel up your workouts and recovery routine to optimize your goals with the ASYSTEM Workout Optimization Bundle. Created to give you the best stamina, energy, recovery, and performance while remaining in a centered state of mind, allowing you to stay consistent with gains and meet your goals.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cb\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/b\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWhat's Inside:\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e(3) Radical Relief Gel Roll On \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e(1) 32-day supply of Productivity Gummies\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2025-11-21T11:57:20-05:00","created_at":"2024-12-17T15:46:17-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":14200,"price_min":14200,"price_max":14200,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":17800,"compare_at_price_min":17800,"compare_at_price_max":17800,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":46901300035824,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":null,"requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"Workout Optimization Bundle","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":14200,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":17800,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Workout-Optimization-Bundle-PDP-Stylized-Image-V1.png?v=1747410609","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Workout-Optimization-Bundle-PDP-Stylized-Image-V2.png?v=1747410609","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Athletes-Tool-Kit-Bundle-background.jpg?v=1747410609","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/ProductivityPDPMainImage1_1_e02339e5-574a-4fe2-8a51-95ca8ca9e076.jpg?v=1747410609","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/PDP-Gel-01_76a06581-f887-46d2-858d-89ff96cd4604.jpg?v=1747410609"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Workout-Optimization-Bundle-PDP-Stylized-Image-V1.png?v=1747410609","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":39623562166512,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1500,"width":1200,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Workout-Optimization-Bundle-PDP-Stylized-Image-V1.png?v=1747410609"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Workout-Optimization-Bundle-PDP-Stylized-Image-V1.png?v=1747410609","width":1200},{"alt":null,"id":39623562199280,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1500,"width":1200,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Workout-Optimization-Bundle-PDP-Stylized-Image-V2.png?v=1747410609"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Workout-Optimization-Bundle-PDP-Stylized-Image-V2.png?v=1747410609","width":1200},{"alt":null,"id":38249104638192,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1350,"width":1080,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Athletes-Tool-Kit-Bundle-background.jpg?v=1747410609"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1350,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Athletes-Tool-Kit-Bundle-background.jpg?v=1747410609","width":1080},{"alt":null,"id":35100019491056,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/ProductivityPDPMainImage1_1_e02339e5-574a-4fe2-8a51-95ca8ca9e076.jpg?v=1747410609"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/ProductivityPDPMainImage1_1_e02339e5-574a-4fe2-8a51-95ca8ca9e076.jpg?v=1747410609","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":36724772143344,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/PDP-Gel-01_76a06581-f887-46d2-858d-89ff96cd4604.jpg?v=1747410609"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/PDP-Gel-01_76a06581-f887-46d2-858d-89ff96cd4604.jpg?v=1747410609","width":1050}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eLevel up your workouts and recovery routine to optimize your goals with the ASYSTEM Workout Optimization Bundle. Created to give you the best stamina, energy, recovery, and performance while remaining in a centered state of mind, allowing you to stay consistent with gains and meet your goals.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cb\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/b\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWhat's Inside:\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e(3) Radical Relief Gel Roll On \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e(1) 32-day supply of Productivity Gummies\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":9091647635696,"title":"The Focus \u0026 Flow Bundle","handle":"the-focus-flow-bundle-virtual","description":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eStruggling to find inspiration, motivation, and creativity? This one is for you. We live in an age where burnout and distraction are more common than ever. Start with a daily Complete Optimization Supplement pack to get your motivation and performance back on track. Get the creative juices going in a focused flow state by combining the concentration of productivity gummies with the relaxation of De-Stress Gummies.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cb\u003e\u003c\/b\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWhat's Inside:\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e30-day supply of Complete Optimization Supplements for Men \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e32-day supply of Productivity Gummies \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e32-day supply of De-Stress Gummies \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2025-11-21T11:56:23-05:00","created_at":"2024-11-05T14:50:56-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":15100,"price_min":15100,"price_max":15100,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":18900,"compare_at_price_min":18900,"compare_at_price_max":18900,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":46765694288112,"title":"Sicilian Lemon + Ginger","option1":"Sicilian Lemon + Ginger","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"The Focus \u0026 Flow Bundle - Sicilian Lemon + Ginger","public_title":"Sicilian Lemon + Ginger","options":["Sicilian Lemon + Ginger"],"price":15100,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":18900,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":48320526024944,"title":"Blood Orange + Cayenne","option1":"Blood Orange + Cayenne","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":null,"requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"The Focus \u0026 Flow Bundle - Blood Orange + Cayenne","public_title":"Blood Orange + Cayenne","options":["Blood Orange + Cayenne"],"price":15100,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":18900,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Focus-Flow-Bundle-Stylized-PDP-Image.png?v=1731957857","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Focus-Flow-Bundle-SLG-background.jpg?v=1731033495","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/01-Hero.jpg?v=1731452393","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/ProductivityPDPMainImage1_1_1575f18c-bcb5-41db-aab2-d26c42caa0c9.jpg?v=1717448081","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Destress-Gummies-Thumbnail.jpg?v=1727195902"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Focus-Flow-Bundle-Stylized-PDP-Image.png?v=1731957857","options":["De-Stress Gummies (Copy) (Choose Your Flavor)"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":37929839984880,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1500,"width":1200,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Focus-Flow-Bundle-Stylized-PDP-Image.png?v=1731957857"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1500,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Focus-Flow-Bundle-Stylized-PDP-Image.png?v=1731957857","width":1200},{"alt":null,"id":37831981433072,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1350,"width":1080,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Focus-Flow-Bundle-SLG-background.jpg?v=1731033495"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1350,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Focus-Flow-Bundle-SLG-background.jpg?v=1731033495","width":1080},{"alt":null,"id":37876565934320,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/01-Hero.jpg?v=1731452393"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/01-Hero.jpg?v=1731452393","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":35931565883632,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/ProductivityPDPMainImage1_1_1575f18c-bcb5-41db-aab2-d26c42caa0c9.jpg?v=1717448081"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/ProductivityPDPMainImage1_1_1575f18c-bcb5-41db-aab2-d26c42caa0c9.jpg?v=1717448081","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":37273597444336,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1350,"width":1080,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Destress-Gummies-Thumbnail.jpg?v=1727195902"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1350,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/Destress-Gummies-Thumbnail.jpg?v=1727195902","width":1080}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003eStruggling to find inspiration, motivation, and creativity? This one is for you. We live in an age where burnout and distraction are more common than ever. Start with a daily Complete Optimization Supplement pack to get your motivation and performance back on track. Get the creative juices going in a focused flow state by combining the concentration of productivity gummies with the relaxation of De-Stress Gummies.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cb\u003e\u003c\/b\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e \u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cstrong\u003eWhat's Inside:\u003c\/strong\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e30-day supply of Complete Optimization Supplements for Men \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e32-day supply of Productivity Gummies \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp dir=\"ltr\"\u003e\u003cspan\u003e32-day supply of De-Stress Gummies \u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":7965723951344,"title":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Hoodie","handle":"asystem-enhanced-energy-hoodie","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eGet comfy in this 100% cotton drawstring hoodie complete with a graphic and positive expression on the back. This hoodie was designed to be worn loosely, so size up and wear year round. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2022-05-17T18:59:34-04:00","created_at":"2022-05-17T18:59:34-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Apparel","tags":["no-shipping-label-for-uk-can","NonCore"],"price":11000,"price_min":11000,"price_max":11000,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":42846398677232,"title":"S","option1":"S","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-HOODIE-S","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":false,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Hoodie - S","public_title":"S","options":["S"],"price":11000,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846398710000,"title":"M","option1":"M","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-HOODIE-M","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Hoodie - M","public_title":"M","options":["M"],"price":11000,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846398775536,"title":"L","option1":"L","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-HOODIE-L","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Hoodie - L","public_title":"L","options":["L"],"price":11000,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846398808304,"title":"XL","option1":"XL","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-HOODIE-XL","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Hoodie - XL","public_title":"XL","options":["XL"],"price":11000,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie1.png?v=1654110790","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie4.png?v=1654205057","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie2.png?v=1654205057","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie3.png?v=1654205057"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie1.png?v=1654110790","options":["Size"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":30322659950832,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie1.png?v=1654110790"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie1.png?v=1654110790","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322660049136,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie4.png?v=1654205057"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie4.png?v=1654205057","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322659983600,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie2.png?v=1654205057"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie2.png?v=1654205057","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322660016368,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie3.png?v=1654205057"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPHoodie3.png?v=1654205057","width":1048}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eGet comfy in this 100% cotton drawstring hoodie complete with a graphic and positive expression on the back. This hoodie was designed to be worn loosely, so size up and wear year round. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":7965708452080,"title":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Tee","handle":"asystem-enhanced-energy-tee","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eA two-tone 100% cotton tee that's perfect on its own or for layering on days outside when the evening draws in. Designed to be worn loosely, so size up. Complete with graphic and positive expression on the back. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2022-05-17T18:53:45-04:00","created_at":"2022-05-17T18:36:26-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Apparel","tags":["no-shipping-label-for-uk-can","NonCore"],"price":4500,"price_min":4500,"price_max":4500,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":42846318887152,"title":"S","option1":"S","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-TEE-S","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Tee - S","public_title":"S","options":["S"],"price":4500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846318919920,"title":"M","option1":"M","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-TEE-M","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Tee - M","public_title":"M","options":["M"],"price":4500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846318952688,"title":"L","option1":"L","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-TEE-L","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Tee - L","public_title":"L","options":["L"],"price":4500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846318985456,"title":"XL","option1":"XL","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-TEE-XL","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Tee - XL","public_title":"XL","options":["XL"],"price":4500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt1.png?v=1654110082","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt2.png?v=1654110082","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt3.png?v=1654110082","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt4.png?v=1654110082","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt5.png?v=1654110083","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt6.png?v=1654110082"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt1.png?v=1654110082","options":["Size"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":30322611912944,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt1.png?v=1654110082"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt1.png?v=1654110082","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322611945712,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt2.png?v=1654110082"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt2.png?v=1654110082","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322611978480,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt3.png?v=1654110082"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt3.png?v=1654110082","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322612011248,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt4.png?v=1654110082"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt4.png?v=1654110082","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322612044016,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt5.png?v=1654110083"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt5.png?v=1654110083","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322612076784,"position":6,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt6.png?v=1654110082"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPShirt6.png?v=1654110082","width":1048}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eA two-tone 100% cotton tee that's perfect on its own or for layering on days outside when the evening draws in. Designed to be worn loosely, so size up. Complete with graphic and positive expression on the back. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":7965727490288,"title":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Hat","handle":"asystem-enhanced-energy-hat","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e100% cotton Klein blue hat. Embroidered graphic. Snapback closure. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2022-05-17T19:05:55-04:00","created_at":"2022-05-17T19:05:55-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Apparel","tags":["no-shipping-label-for-uk-can","NonCore"],"price":3500,"price_min":3500,"price_max":3500,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":42846426136816,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-DADHAT-1","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Hat","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":3500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap1.png?v=1654109207","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap2.png?v=1654109207","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap3.png?v=1654109207"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap1.png?v=1654109207","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":30322551161072,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap1.png?v=1654109207"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap1.png?v=1654109207","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322551193840,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap2.png?v=1654109207"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap2.png?v=1654109207","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322551226608,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap3.png?v=1654109207"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPCap3.png?v=1654109207","width":1048}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e100% cotton Klein blue hat. Embroidered graphic. Snapback closure. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":7965725360368,"title":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Sweatpants","handle":"asystem-enhanced-energy-sweatpants","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e100% premium soft cotton sweatpants with adjustable drawstring. Elastic waist \u0026amp; cuff complete with a graphic and positive expression on the leg. Designed to be worn loosely, so size up. Made In Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2022-05-17T19:01:58-04:00","created_at":"2022-05-17T19:01:58-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Apparel","tags":["no-shipping-label-for-uk-can","NonCore"],"price":7500,"price_min":7500,"price_max":7500,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":42846409294064,"title":"S","option1":"S","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-SWEATPANTS-S","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Sweatpants - S","public_title":"S","options":["S"],"price":7500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846409326832,"title":"M","option1":"M","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-SWEATPANTS-M","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Sweatpants - M","public_title":"M","options":["M"],"price":7500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846409359600,"title":"L","option1":"L","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-SWEATPANTS-L","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Sweatpants - L","public_title":"L","options":["L"],"price":7500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]},{"id":42846409392368,"title":"XL","option1":"XL","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-SWEATPANTS-XL","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Sweatpants - XL","public_title":"XL","options":["XL"],"price":7500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":null,"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant1.png?v=1654109840","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant2.png?v=1654109840","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant3.png?v=1654109840","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant4.png?v=1654109840"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant1.png?v=1654109840","options":["Size"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":30322598609136,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant1.png?v=1654109840"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant1.png?v=1654109840","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322598641904,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant2.png?v=1654109840"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant2.png?v=1654109840","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322598674672,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant3.png?v=1654109840"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant3.png?v=1654109840","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322598707440,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant4.png?v=1654109840"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSweatpant4.png?v=1654109840","width":1048}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e100% premium soft cotton sweatpants with adjustable drawstring. Elastic waist \u0026amp; cuff complete with a graphic and positive expression on the leg. Designed to be worn loosely, so size up. Made In Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":7965726277872,"title":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Socks","handle":"asystem-enhanced-energy-socks","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eHigh quality knit featuring graphic and logo on the foot. Double padded heel And toe. One size. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2022-06-01T15:11:09-04:00","created_at":"2022-05-17T19:03:27-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Apparel","tags":["no-shipping-label-for-uk-can","NonCore"],"price":1500,"price_min":1500,"price_max":1500,"available":true,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":42846415880432,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-ENERGY-SOCKS-1","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":true,"name":"ASYSTEM Enhanced Energy Socks","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":1500,"weight":241,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks1.png?v=1654110598","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks2.png?v=1654110598","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks3.png?v=1654110598"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks1.png?v=1654110598","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":30322646548720,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks1.png?v=1654110598"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks1.png?v=1654110598","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322646581488,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks2.png?v=1654110598"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks2.png?v=1654110598","width":1048},{"alt":null,"id":30322646614256,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"width":1048,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks3.png?v=1654110598"},"aspect_ratio":0.688,"height":1524,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/EnergyPDPSocks3.png?v=1654110598","width":1048}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eHigh quality knit featuring graphic and logo on the foot. Double padded heel And toe. One size. Made in Los Angeles.\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"},{"id":8132371382512,"title":"IMMUNITY+","handle":"immunity","description":"High potency immune support engineered to protect you from illness, help you recover quicker and feel your best - everyday*. Inspired by Bruce Wayne, IMMUNITY+ has been created in collaboration with DC Comics and Warner Bros. to activate your immune system.","published_at":"2022-10-31T14:21:19-04:00","created_at":"2022-10-05T23:11:27-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":4500,"price_min":4500,"price_max":4500,"available":false,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":5500,"compare_at_price_min":5500,"compare_at_price_max":5500,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":43534522220784,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-IM-30D-1","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":false,"name":"IMMUNITY+","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":4500,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":5500,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"850014293284","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/02-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667238830","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/9.jpg?v=1667396796","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/05-Hero-white-logos_2.jpg?v=1671666126","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/1_1.jpg?v=1671666126","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos.jpg?v=1671666126","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/2.jpg?v=1671666126","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/04-Hero-grey-logos.jpg?v=1671666126","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos__1.jpg?v=1671666126","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/05-Hero-white-logos_2_e79f7382-d746-4e4d-a8e2-4b66eeab6240.jpg?v=1671666126"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/02-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667238830","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":31485691724016,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/02-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667238830"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/02-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667238830","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31560919286000,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/9.jpg?v=1667396796"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/9.jpg?v=1667396796","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31836338422000,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1350,"width":1080,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25.thumbnail.0000000000.jpg?v=1671666119"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"duration":10130,"media_type":"video","sources":[{"format":"mp4","height":480,"mime_type":"video\/mp4","url":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/videos\/c\/vp\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25.SD-480p-1.2Mbps-11321147.mp4?v=0","width":384},{"format":"mp4","height":1080,"mime_type":"video\/mp4","url":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/videos\/c\/vp\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25.HD-1080p-4.8Mbps-11321147.mp4?v=0","width":864},{"format":"mp4","height":720,"mime_type":"video\/mp4","url":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/videos\/c\/vp\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25.HD-720p-3.0Mbps-11321147.mp4?v=0","width":576},{"format":"m3u8","height":1080,"mime_type":"application\/x-mpegURL","url":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/videos\/c\/vp\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25\/15e521998c2843e581bee9ee3cac9d25.m3u8?v=0","width":864}]},{"alt":null,"id":31560956051696,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/05-Hero-white-logos_2.jpg?v=1671666126"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/05-Hero-white-logos_2.jpg?v=1671666126","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31560919220464,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/1_1.jpg?v=1671666126"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/1_1.jpg?v=1671666126","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31509614821616,"position":6,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos.jpg?v=1671666126"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos.jpg?v=1671666126","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31560919253232,"position":7,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/2.jpg?v=1671666126"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/2.jpg?v=1671666126","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31509614854384,"position":8,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/04-Hero-grey-logos.jpg?v=1671666126"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/04-Hero-grey-logos.jpg?v=1671666126","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31650534785264,"position":9,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos__1.jpg?v=1671666126"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos__1.jpg?v=1671666126","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31650534818032,"position":10,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/05-Hero-white-logos_2_e79f7382-d746-4e4d-a8e2-4b66eeab6240.jpg?v=1671666126"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/05-Hero-white-logos_2_e79f7382-d746-4e4d-a8e2-4b66eeab6240.jpg?v=1671666126","width":1050}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"High potency immune support engineered to protect you from illness, help you recover quicker and feel your best - everyday*. Inspired by Bruce Wayne, IMMUNITY+ has been created in collaboration with DC Comics and Warner Bros. to activate your immune system."},{"id":8138369499376,"title":"Bruce Wayne System","handle":"preworkout-immunity-bundle","description":"Developed in collaboration with Warner Bros and DC Comics and inspired by the hero of Gotham City himself, Bruce Wayne. Two powerful supplements with cutting edge ingredients clinically proven to enhance energy and maintain a strong active immune system*\u003cbr\u003e","published_at":"2022-10-31T14:24:27-04:00","created_at":"2022-10-11T00:00:30-04:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"","tags":[],"price":8500,"price_min":8500,"price_max":8500,"available":false,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":43551972983024,"title":"Default Title","option1":"Default Title","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"ASYS-WE-30D-1","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":false,"name":"Bruce Wayne System","public_title":null,"options":["Default Title"],"price":8500,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/12-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667239820","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/man-800x1000_2_3d05bda1-ad98-4aee-89a0-c37b76b25756.jpg?v=1667239820","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/11-Hero-white-logos_2.jpg?v=1667239820","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/bundles-women_dad0e9d3-4fbe-4413-8e9b-5f3b48162cfb.jpg?v=1667239820","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/08-Hero-grey-logos_25147443-e9f8-4e39-aa46-71baf9729037.jpg?v=1667239820","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/run-800x1000_1_8905a335-9144-401a-a633-30c3b255b757.jpg?v=1667239820","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos_3f819f75-bc3d-431e-87be-f9a90955a90c.jpg?v=1667239820"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/12-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667239820","options":["Title"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":31485694968048,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/12-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667239820"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/12-Hero-white-logos.jpg?v=1667239820","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31552111739120,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1000,"width":800,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/man-800x1000_2_3d05bda1-ad98-4aee-89a0-c37b76b25756.jpg?v=1667239820"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1000,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/man-800x1000_2_3d05bda1-ad98-4aee-89a0-c37b76b25756.jpg?v=1667239820","width":800},{"alt":null,"id":31553224442096,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/11-Hero-white-logos_2.jpg?v=1667239820"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/11-Hero-white-logos_2.jpg?v=1667239820","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31553229357296,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1000,"width":800,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/bundles-women_dad0e9d3-4fbe-4413-8e9b-5f3b48162cfb.jpg?v=1667239820"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1000,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/bundles-women_dad0e9d3-4fbe-4413-8e9b-5f3b48162cfb.jpg?v=1667239820","width":800},{"alt":null,"id":31509627044080,"position":5,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/08-Hero-grey-logos_25147443-e9f8-4e39-aa46-71baf9729037.jpg?v=1667239820"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/08-Hero-grey-logos_25147443-e9f8-4e39-aa46-71baf9729037.jpg?v=1667239820","width":1050},{"alt":null,"id":31552111771888,"position":6,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1000,"width":800,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/run-800x1000_1_8905a335-9144-401a-a633-30c3b255b757.jpg?v=1667239820"},"aspect_ratio":0.8,"height":1000,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/run-800x1000_1_8905a335-9144-401a-a633-30c3b255b757.jpg?v=1667239820","width":800},{"alt":null,"id":31509627076848,"position":7,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"width":1050,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos_3f819f75-bc3d-431e-87be-f9a90955a90c.jpg?v=1667239820"},"aspect_ratio":0.779,"height":1348,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/products\/03-Hero-grey-logos_3f819f75-bc3d-431e-87be-f9a90955a90c.jpg?v=1667239820","width":1050}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[],"content":"Developed in collaboration with Warner Bros and DC Comics and inspired by the hero of Gotham City himself, Bruce Wayne. Two powerful supplements with cutting edge ingredients clinically proven to enhance energy and maintain a strong active immune system*\u003cbr\u003e"},{"id":7855599649008,"title":"Sleep Gummies (Melatonin Free)","handle":"complete-calm-sleep-gummies-melatonin-free","description":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eAn advanced sleep gummy. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eMade with natural botanicals and adaptogens like \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eL-Tryptophan, Chamomile, Passionflower, Holy Basil, and a patented pure saffron, Safr-Inside™, clinically studied to help support stress and sleep. Calm your mind so you can relax, Zzz, and wake up refreshed.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eImprove sleep quality. No daytime grogginess.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e","published_at":"2022-02-28T12:10:16-05:00","created_at":"2022-02-28T12:10:17-05:00","vendor":"ASYSTEM","type":"Consumable","tags":["Gummy"],"price":5900,"price_min":5900,"price_max":5900,"available":false,"price_varies":false,"compare_at_price":null,"compare_at_price_min":0,"compare_at_price_max":0,"compare_at_price_varies":false,"variants":[{"id":42479566356720,"title":"32 Gummies","option1":"32 Gummies","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"CCS-WB-32D-M1","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":false,"name":"Sleep Gummies (Melatonin Free) - 32 Gummies","public_title":"32 Gummies","options":["32 Gummies"],"price":5900,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":5310}],"price":5310,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":5310,"selling_plan_id":6412730608,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"},{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":4720}],"price":4720,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":4720,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]},{"id":42563604250864,"title":"Two Refills (32 Gummies)","option1":"Two Refills (32 Gummies)","option2":null,"option3":null,"sku":"CCS-WB-32D-MR","requires_shipping":true,"taxable":true,"featured_image":null,"available":false,"name":"Sleep Gummies (Melatonin Free) - Two Refills (32 Gummies)","public_title":"Two Refills (32 Gummies)","options":["Two Refills (32 Gummies)"],"price":5900,"weight":0,"compare_at_price":null,"inventory_management":"shopify","barcode":"","requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_allocations":[{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":5310}],"price":5310,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":5310,"selling_plan_id":6412730608,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"},{"price_adjustments":[{"position":1,"price":4720}],"price":4720,"compare_at_price":5900,"per_delivery_price":4720,"selling_plan_id":7042990320,"selling_plan_group_id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836"}]}],"images":["\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743521814","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-05.jpg?v=1743521814","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-06.jpg?v=1743521814","\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-07.jpg?v=1743521815"],"featured_image":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743521814","options":["Pick Your Pack"],"media":[{"alt":null,"id":39145430188272,"position":1,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743521814"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-04.jpg?v=1743521814","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39145430155504,"position":2,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-05.jpg?v=1743521814"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-05.jpg?v=1743521814","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39145430221040,"position":3,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-06.jpg?v=1743521814"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-06.jpg?v=1743521814","width":1250},{"alt":null,"id":39145430253808,"position":4,"preview_image":{"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"width":1250,"src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-07.jpg?v=1743521815"},"aspect_ratio":1.0,"height":1250,"media_type":"image","src":"\/\/www.asystem.com\/cdn\/shop\/files\/sleep_PDP_edits-07.jpg?v=1743521815","width":1250}],"requires_selling_plan":false,"selling_plan_groups":[{"id":"26f8c07511f4e08730e3622e037123a1a3a51836","name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"values":["32 Days","30 Days"]}],"selling_plans":[{"id":6412730608,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"32 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":10}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}},{"id":7042990320,"name":"Subscribe \u0026 Save 20%","description":null,"options":[{"name":"Delivery Every","position":1,"value":"30 Days"}],"recurring_deliveries":true,"price_adjustments":[{"order_count":null,"position":1,"value_type":"percentage","value":20}],"checkout_charge":{"value_type":"percentage","value":100}}],"app_id":"5859381"}],"content":"\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eAn advanced sleep gummy. \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eMade with natural botanicals and adaptogens like \u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eL-Tryptophan, Chamomile, Passionflower, Holy Basil, and a patented pure saffron, Safr-Inside™, clinically studied to help support stress and sleep. Calm your mind so you can relax, Zzz, and wake up refreshed.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e\n\u003cp\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003e\u003cbr\u003e\u003c\/span\u003e\u003cspan style=\"font-weight: 400;\"\u003eImprove sleep quality. No daytime grogginess.*\u003c\/span\u003e\u003c\/p\u003e"}]
{"note":null,"attributes":{},"original_total_price":0,"total_price":0,"total_discount":0,"total_weight":0.0,"item_count":0,"items":[],"requires_shipping":false,"currency":"USD","items_subtotal_price":0,"cart_level_discount_applications":[],"checkout_charge_amount":0}